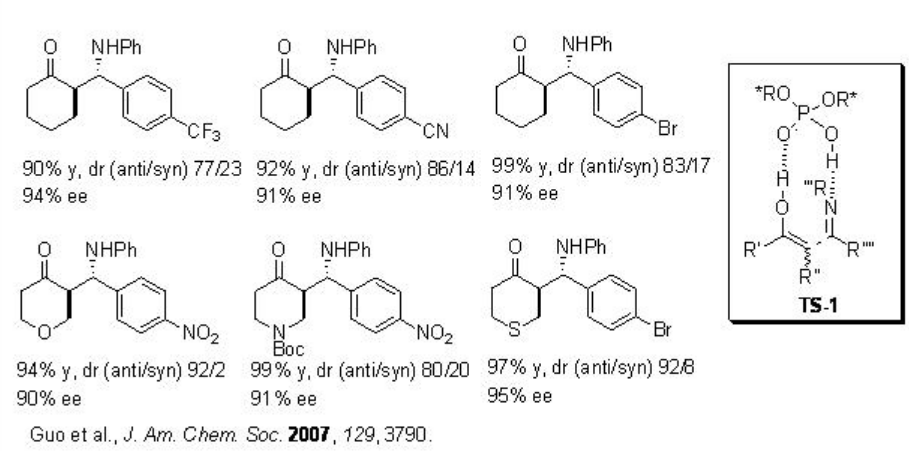
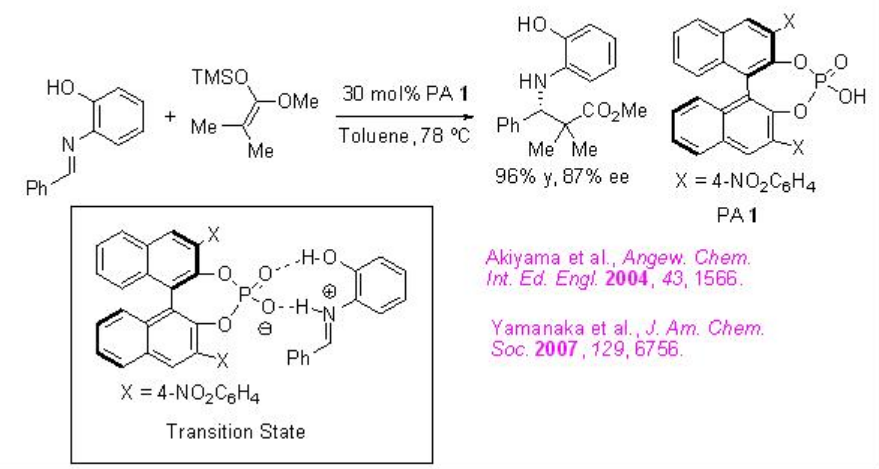
In organic chemistry, chiral phosphoric acids are esters of phosphoric acid H3PO4 that have chiral backbones. Well known examples include cyclic diesters derived from the BINOL and TADDOL motifs. These compounds are used in asymmetric catalysis as chiral Brønsted acids and/or hydrogen-bond donors. The conjugate bases are also used in generating chiral ion pairs.
In one example, they are used to catalyze the asymmetric desymmetrization by monohydrolysis of a diester.
References